Chapter2 시간복잡도~!
시간복잡도
올바른 정답을 구하는 알고리즘이 여럿이면 쉬운방법이나, 시간/메모리상으로 효율적인 방법택함
자바는 컴파일 방식으로만 동작하는 언어보다 느린편(ex C/C++)
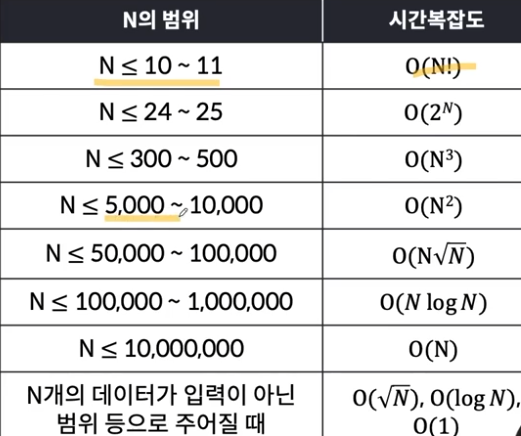
시간복잡도에 관해 하기 참고해보면 좋다(의존x)
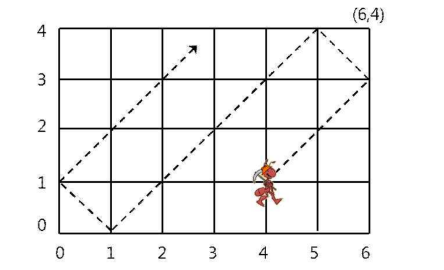
저걸 while 문으로 돌리면 시간복잡도가 아주 커진다.
그래서 (4,1) 지점에 24시간 후 돌아와서 계속 반복하는 24시간 주기를 발견할수 있으나
시간복잡도가 너무 드다
이 주기성을 모듈러를 하기와 같이 적용
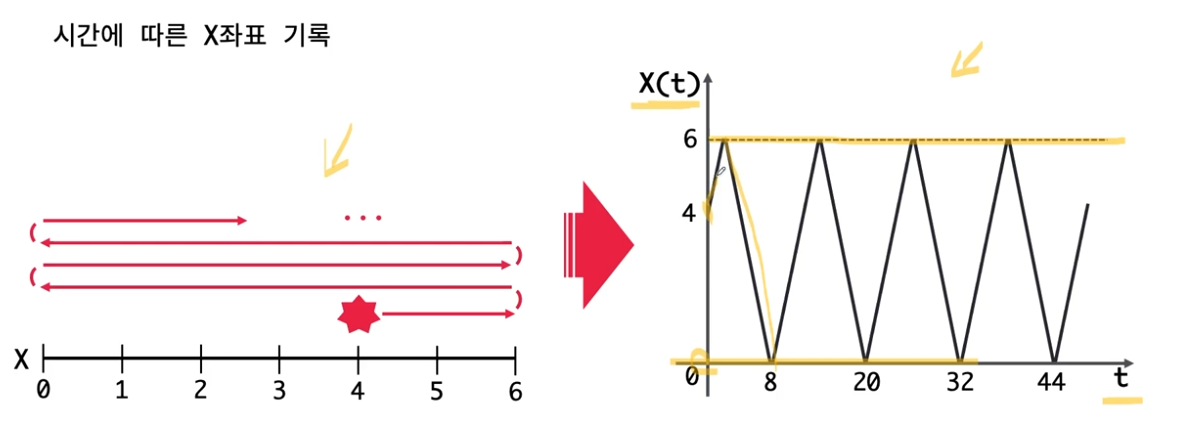
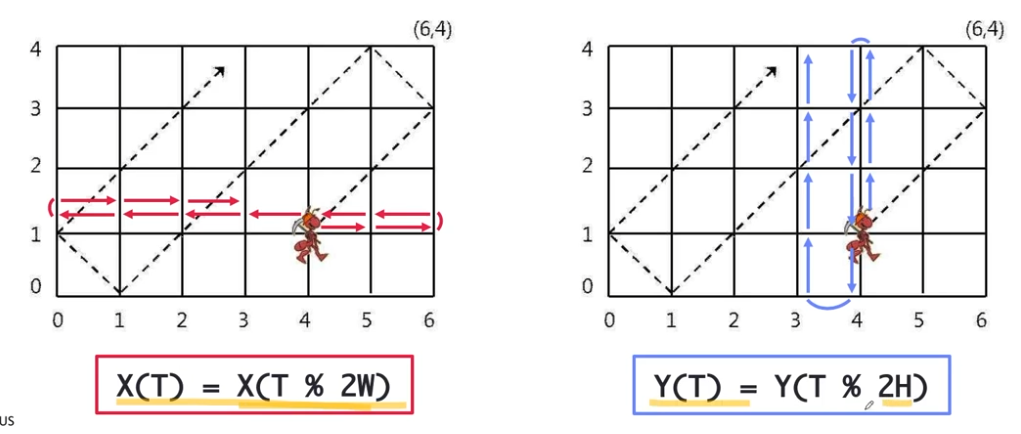
x와 y 좌표 방식에 대해 모듈러 원리를 적용하여
하기와 같은 시간 복잡도 공식이 만들어진다.
https://velog.io/@iamipro/%EB%B0%B1%EC%A4%80-10158-%EC%9E%90%EB%B0%94-%EA%B0%9C%EB%AF%B8
시간복잡도를 가지고 생각하면서 풀수 있는데
하기와 같이 코드로 정리 해 볼수 있다.
특이한 것은 자바8은 시간초과가 안되나 자바11은 자바시간초과가 되버린다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
// 넓이
int W = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 높이
int H = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// W * H 의 격자 공간
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
// 현재 위치
int P = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 현재 위치
int Q = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
// 계산할 시간
int T = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 실시간 x좌표는 P에서 시간(T)을 넓이 2배 즉 좌에서 우와 우에서 좌를 반복하는 양의 나머지에 위치
int currentX = (P+T) % (2 * W);
// 실시간 y좌표는 Q에서 시간(T)을 늪이 2배 즉 위에서 아래와 아래에서 위를 반복하는 양의 나머지에 위치
int currentY = (Q+T) % (2 * H);
if(currentX > W) currentX = 2*W - currentX;
if(currentY > H) currentY = 2*H - currentY;
System.out.println(currentX+" "+currentY);
}
}
Chatpter3 배열~!
자료구조 - 배열

https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1236
1236번: 성 지키기
첫째 줄에 성의 세로 크기 N과 가로 크기 M이 주어진다. N과 M은 50보다 작거나 같은 자연수이다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에는 성의 상태가 주어진다. 성의 상태는 .은 빈칸, X는 경비원이 있는 칸이다
www.acmicpc.net
성지키기를 문제를 해결하는데 있어서
두가지 방법으로 풀수 있다.
시간복잡도(N *M)
public class Baekjoon1236 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N= sc.nextInt(); // 세로
int M= sc.nextInt(); // 가로
char[][] map = new char[N][M];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
map[i]= sc.next().toCharArray();
}
//1. 각 행/열에 대해 경비원이 있는지 확인한다.
/* boolean[] existRow = new boolean[N];
boolean[] existCol = new boolean[M];*/
int existRowCount=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
boolean exist = false;
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++)
if (map[i][j] == 'X') {
exist = true;
break;
}
if (exist) existRowCount++;
}
int existColCount=0;
for(int c=0; c<M; c++){
boolean exist=false;
for(int r=0; r<N; r++)
if(map[r][c] =='X'){
exist=true;
break;
}
if(exist)existColCount++;
}
//2. 보호받지 못하는 행/열의 갯수를 구한다.
int needRowCount= N-existRowCount;
int needColCount= M-existColCount;
//3. 둘 중 큰 값을 출력한다.
System.out.println(Math.max(needRowCount, needColCount));
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Baekjoon1236 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N= sc.nextInt(); // 세로
int M= sc.nextInt(); // 가로
char[][] map = new char[N][M];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
map[i]= sc.next().toCharArray();
}
//1. 각 행/열에 대해 경비원이 있는지 확인한다.
boolean[] existRow = new boolean[N];
boolean[] existCol = new boolean[M];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
for(int j=0; j<M; j++){
if(map[i][j]=='X'){
existRow[i]=true;
existCol[j]=true;
}
}
}
//2. 보호받지 못하는 행/열의 갯수를 구한다.
int needRowCount= N;
int needColCount= M;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
if(existRow[i]) needRowCount--;
}
for(int i=0; i<M; i++){
if(existCol[i]) needColCount--;
}
//3. 둘 중 큰 값을 출력한다.
System.out.println(Math.max(needRowCount, needColCount));
}
}
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/10431
10431번: 줄세우기
초등학교 선생님 강산이는 아이들을 데리고 단체로 어떤 일을 할 때 불편함이 없도록 새로 반에 배정받은 아이들에게 키 순서대로 번호를 부여한다. 번호를 부여할 땐 키가 가장 작은 아이가 1
www.acmicpc.net
1. 문제 : 키순서대로 번호부여 (1~20)
2. 방법 : 키가 큰 사람 있으면 그 사람 앞(나머지 뒤로) ,
키가큰 사람 없으면 그 자리에 그대로
3. 목표: 몇번을 반복하는가?
4. 상황 : 테스트케이스 P와 각 번호T
시간복잡도 : O(P * N2)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Baekjoon10431 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 테스트 케이스 P
int P = sc.nextInt();
// 테스트 케이스반큼 반복
while(P-- > 0){
// 테스트 케이스 T 번호
int T = sc.nextInt();
// 테스트케시스 T의 학생 생성
int[] h = new int[20];
for(int i=0; i<20; i++)
h[i] = sc.nextInt();
int cnt =0;
// 학생 줄세우기
int[] sorted = new int[20];
for(int i=0; i<20;i++){
//1. 줄 서 있는 학생 중에 자신보다 큰 학생을 찾는다.
boolean find =false;
//1-1. 찾지 못햇다면, 줄의 가장 뒤에선다.
for(int j=0; j<i; j++){
if(sorted[j]>h[i]){
find = true;
//2. 찾았다면, 그 학생의 앞에 선다.
//3. 그 학생과 그 뒤의 학생이 모두 한칸씩 물러난다.
for(int k =i-1 ; k>= j; k--){
sorted[k+1] = sorted[k];
cnt++;
}
sorted[j] = h[i];
break;
}
}
if(!find){
sorted[i] = h[i];
}
}
System.out.println(T+" "+cnt);
}
}
}https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/10989
10989번: 수 정렬하기 3
첫째 줄에 수의 개수 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 10,000,000)이 주어진다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에는 수가 주어진다. 이 수는 10,000보다 작거나 같은 자연수이다.
www.acmicpc.net
1.문제 , 2.방법 3.목표 4.상황 을 봅시다.
1. 문제 : N개의 수가 주어지나 비정렬
2. 방법 : 오름차순
3. 목표: 정렬
4. 상황 : 수의 개수 N, N개의 줄에 수
시간복잡도 0(max(N,10,000))
import java.io.*;
public class Baekjoon10989 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[] cnt = new int[10001];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
cnt[Integer.parseInt(br.readLine())]++;
}
for(int i=1; i<10001; i++){
while(cnt[i]-- > 0){
bw.write(i+"\n");
}
}
bw.flush();
}
}
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/3273
3273번: 두 수의 합
n개의 서로 다른 양의 정수 a1, a2, ..., an으로 이루어진 수열이 있다. ai의 값은 1보다 크거나 같고, 1000000보다 작거나 같은 자연수이다. 자연수 x가 주어졌을 때, ai + aj = x (1 ≤ i < j ≤ n)을 만족하는
www.acmicpc.net
1.문제 : a1, a2, ..., an으로 이루어진 수열이 있다. 두수의 합이 X가 되는 쌍의 개수를 알고 싶다.
2.방법 : ai + aj = x (1 ≤ i < j ≤ n)
3.목표 : 자연수 x가 주어졌을 때 ai + aj = x 를 만족시키는 (ai, aj)쌍의 수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성
4.상황 : ai의 값은 1보다 크거나 같고, 1000000보다 작거나 같은 자연수
시간복잡도 O(N) 또는 O(1,000,000)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Baekjoon3273 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 테스트 케이스 수 P
int N= sc.nextInt();
// 테스트 케이스 P 배열
int[] arr = new int[N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
arr[i]= sc.nextInt();
}
// 번호
int X = sc.nextInt();
//
boolean[] check = new boolean[1000001];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
check[arr[i]]=true;
}
int cnt =0;
for(int i=0; i<= (X-1) /2; i++){
if(i <= 1000000 && X-i <=100000 ){
cnt += (check[i] && check[X-i]) ? 1: 0;
}
}
System.out.println(cnt);
}
}
'4차산업혁명의 일꾼 > 웹개발' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 우아한테크코스 10분톡 - JPA와 JDBC 정리 (0) | 2023.06.21 |
|---|---|
| Java 코딩테스트 (2) | 2023.05.12 |
| Java 코딩테스트 (0) | 2023.04.27 |
| Java 코딩테스트 (0) | 2023.04.17 |
| [컴퓨터/IT] 객체지향의 사실과 오해 정리 (0) | 2023.04.17 |